Intraductal Papillary Neoplasm of Bile Duct : Macroscopic

Comments:
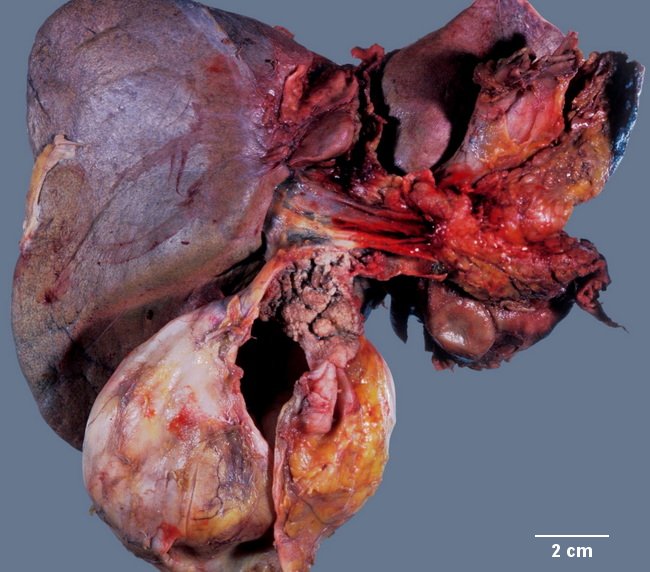
Macroscopic Appearance: Intraductal papillary neoplasm of the bile duct (IPNB) appears as a papillary, polypoid or villous exophytic mass growing into a dilated bile duct lumen. It can develop anywhere along the biliary tree, including intrahepatic and extrahepatic bile ducts and often fills the lumen of the involved duct. IPNB may form a single mass localized to one part of the biliary tree or it may appear as a conglomerate of mixed papillary, villous, polypoid or granular exophytic lesions (previously called papillomatosis) that can extend over considerable length and cover a wide area of the bile duct mucosa. Infrequently, there are multiple discrete lesions. The size range is < 1 cm to 16 cm. The adjacent mucosa is often rough and shows small granular or papillary lesions continuous with the main tumor. The image shows a papiilary tumor with granular appearance arising in the common bile duct and extending into the cystic duct. The gallbladder appears distented. See close-up in the next image. Image courtesy of: Dr. Ibrahim Zardawi; used with permission.



