Intraductal Papillary Neoplasm of Bile Duct : Mucin Hypersecretion

Comments:
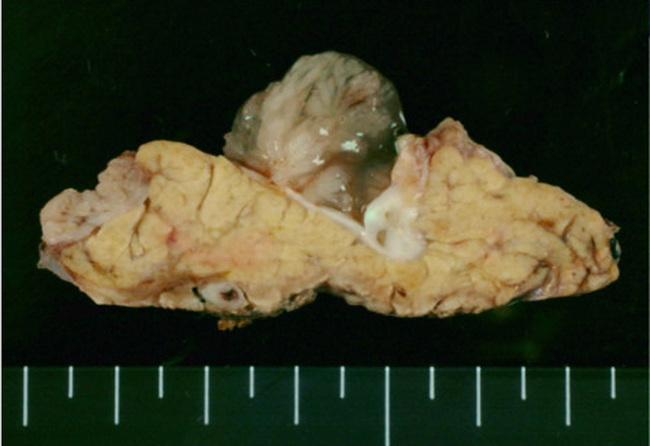
Mucin Hypersecretion in Intraductal Papillary Neoplasm of Bile Ducts (IPNB): About 40% of IPNBs, especially the gastric and intestinal subtypes, secrete copious mucin which envelops the papillary tumor and fills and expands the bile duct lumen. It shows striking similarity to intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm of pancreas. Mucin hypersecretion is more common in intrahepatic than extrahepatic lesions and more frequent in Asian countries than in Western countries. Mucin-hypersecreting IPNBs are often associated with high-grade dysplasia/in-situ carcinoma or at most minimally invasive carcinoma, whereas IPNBs without mucin-hypersecretion frequently have invasive carcinoma. The image shows an IPNB covered with a blob of mucin within extrahepatic bile duct. Image source: Nakanuma Y. et al. Intraductal Papillary Neoplasm of Bile Duct: Updated Clinicopathologic Characteristics and Molecular and Genetic Alterations. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 3991; doi:10.3390/jcm9123991; image cropped and used under Creative Commons Attribution License.



