Lipoma : Role of HMGA2

Comments:
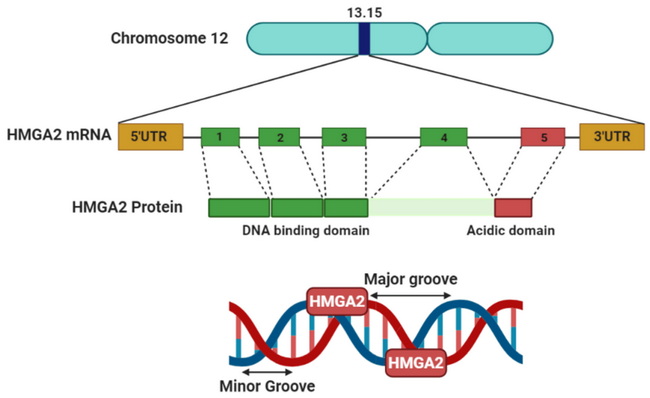
Role of HMGA2: High mobility group (HMG) is a superfamily of non-histone, DNA-binding proteins that regulate gene expression by altering chromatin structure. They have a role in replication, recombination, transcription, and DNA repair. HMGA superfamily consists of HMGA, HMGB and HMGN. HMGA gene family contains HMGA1 and HMGA2.HMGA proteins carry out their functions by binding to the AT-rich regions in the minor groove of DNA double helix and bending the DNA molecule. The conformational changes help regulate transcription of several key genes. They have extremely broad DNA sequence specificity and constitute a major mechanism for DNA-protein interaction. Besides DNA, HMGA proteins also interact with other proteins such as E2 promoter-binding factor 1 (E2F1) and retinoblastoma protein (Rb).Image source: Mansoori B, Mohammadi A, Ditzel HJ, Duijf PHG, Khaze V, Gjerstorff MF, Baradaran B. HMGA2 as a Critical Regulator in Cancer Development. Genes. 2021; 12(2):269. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12020269; used under Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.



