Cirrhosis and Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Tyrosinemia

Comments:
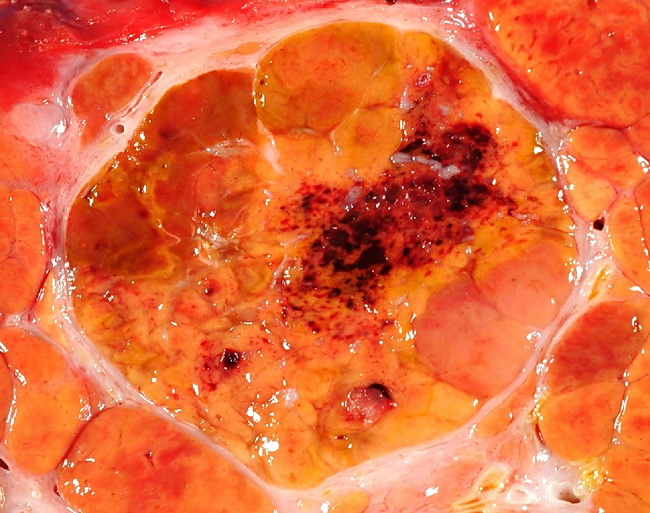
Tyrosinemia type I (hereditary infantile tyrosinemia) is caused by a deficiency of the enzyme fumarylacetoacetate hydrolase and invariably results in cirrhosis, which is the histologic hallmark of the disease. Nodules > 3 mm are designated “macronodular cirrhosis” (as seen here) while those < 3 mm are “micronodular.” This specimen also contains a focus of hepatocellular carcinoma which comprises a well-circumscribed yellow-brown mass with multifocal hemorrhage. Image courtesy of Dr. Jean-Christophe Fournet, Paris, France; humpath.com; Used with permission.



