Solitary Fibrous Tumor : Gross Pathology

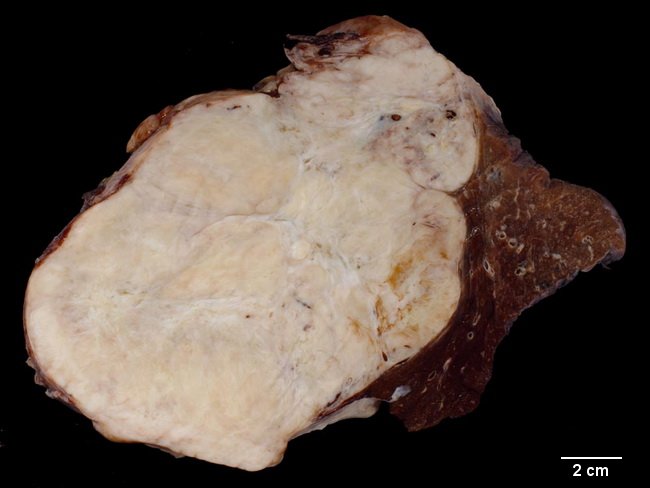
Comments:
Gross Pathology: Solitary fibrous tumors (SFT) in deep soft tissues present as large, well-circumscribed but usually unencapsulated tumors. When arising from serosal surfaces such as pleura, they can grow as an exophytic mass. The size generally ranges from 5 to 10 cm. The cut surface is grayish-white or red-brown and may show hemorrhagic or cystic areas. Case History: The image shows a large malignant solitary fibrous tumor arising in the pleura in an adult male. The patient presented with dyspnea on exertion and was found to have a large tumor in right upper hemithorax. The resected specimen showed a 23 cm size tumor arising from the visceral pleura and compressing the underlying lung parenchyma. CD34, CD99, and Bcl-2 were positive. Image copyright: pathorama.ch. Features of malignancy in a solitary fibrous tumor include: high cellularity with overlapping nuclei, pleomorphism, large size (> 5cm), increased mitotic activity (> 4/10 hpf), and foci of hemorrhage and necrosis.



