Hyaline-Vascular Castleman Disease : Differential

Comments:
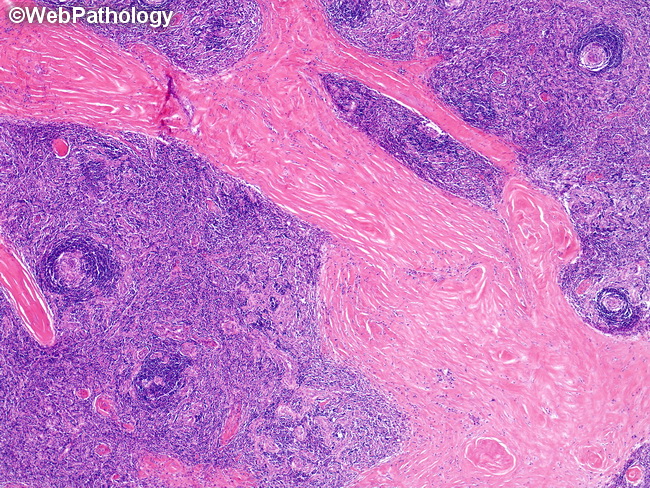
Differential Diagnosis of Hyaline-Vascular Castleman disease (HVCD): HVCD shows marked expansion of the mantle zone of the follicles along with regression of the germinal centers. These features are not specific and may be seen in HIV-associated lymphadenopathy (late stages), angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma (AITL), follicular or mantle cell lymphoma, and non-specific reactive lymphadenopathy. HIV: Clinical history and serologic testing can be used to rule out HIV infection. AITL: AITL may show atrophic germinal centers as well as proliferation of high endothelial venules mimicking HVCD. However, it is a diffuse process and shows expanded networks of CD21+ and CD23+ follicular dendritic cells outside of B-cell follicles. Features favoring AITL over HVCD include: atypical lymphoid cells, clear cells, CD10+/PD1+/BCL6+ T-cells outside of germinal centers, and EBV+ B immunoblasts in the interfollicular region. Mantle Cell Lymphoma (MCL): The expanded mantle zone of HVCD may be mistaken for MCL. The lymphoid cells in MCL are monomorphic, atypical, and express cyclinD1. The interfollicular vascular proliferation of HVCD is absent. Follicular Lymphoma: Immunophenotypic analysis will show monoclonal B-cells that express CD19, CD20, CD79a, BCL2, BCL6, and CD10. This image shows a few small, regressively transformed germinal centers surrounded by an expanded mantle zone, vascular proliferation in the interfollicular region, and bands of fibrosis.



